Achalasia
Understanding Achalasia: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Imagine enjoying your favorite meal with friends or family, only to find that swallowing becomes difficult, causing food to get stuck in your throat. This frustrating experience is a reality for people with achalasia, a treatable disorder of the esophagus. Let’s delve into what achalasia is, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and available treatments.
What is Achalasia?
Achalasia is a condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. It is a relatively rare disease affecting about 1 in 100,000 people. It affects both adults and children. Men and women are equally affected. Normally, when we swallow, the esophagus contracts to push food and liquids into the stomach. In achalasia, however, the muscles of the lower esophagus fail to relax properly, and the valve at the lower end of the esophagus (lower esophageal sphincter – LES) doesn’t open fully. Over time, the motor function of the esophageal muscles weaken and the esophagus enlarges. This makes it difficult for food and liquids to pass into the stomach, leading to symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, regurgitation of food, and sometimes chest pain. Achalasia is a chronic disease; most people suffering from this condition will try to tolerate the difficulty in swallowing and adjust their diet to take small portions or choose to have a liquid diet. Some of them may become thin and malnourished with poor quality of life. Speak to your doctors or contact us through this website, email or telephone for further details.
Symptoms of Achalasia
The primary symptoms of achalasia include:
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia):This is the most common symptom, where you feel like food gets stuck in your chest.
- Regurgitation:Food and liquid can come back up into your throat without warning, especially when lying down or bending over.
- Chest Pain:Some people experience mild to moderate chest pain or discomfort, often mistaken for heartburn.
Causes of Achalasia
The exact cause of achalasia isn’t fully understood. It is thought to be due to damage to the nerves of the esophagus, which control the relaxation of the muscles. This damage may be caused by an autoimmune reaction, genetic factors, or viral infections.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing achalasia involves several tests:
1. Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is passed through your mouth and into your esophagus to examine it directly. This test is usually done as an inpatient day procedure, takes about 10mins and is performed under sedation to minimise any discomfort. This test is mandatory to assess the esophagus carefully, as esophageal cancer or cancer of the gastro-esophageal junction can also give rise to the same symptoms as Achalasia
2. Esophageal Manometry: This is the most important test to confirm the diagnosis of achalasia, and allows us to see what happens when a patient swallows. A small thin tube with pressure sensors is inserted gently into the oesophagus and stomach. The movement of the oesophagus and pressure of the LES will be recorded to determine any impairment in function. This allows us to confirm the diagnosis of Achalasia and to obtain detailed information to help guide your treatment.
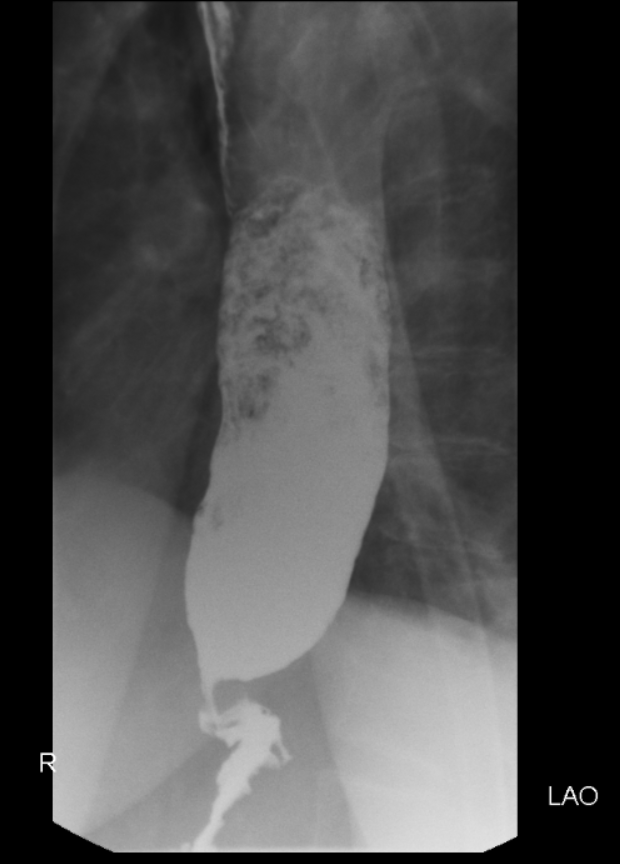
3. Barium Swallow: You’ll drink a contrast liquid (barium) that shows up on X-rays, allowing doctors to see the shape and function of your esophagus. This test may be done only for selected patients.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for achalasia, several treatments can help manage symptoms effectively:
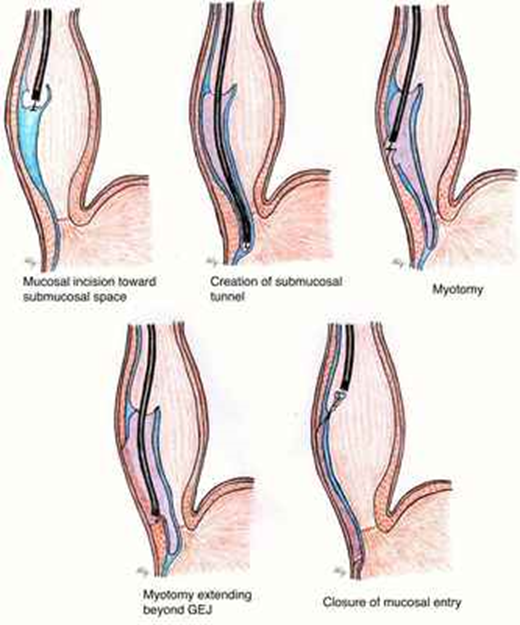
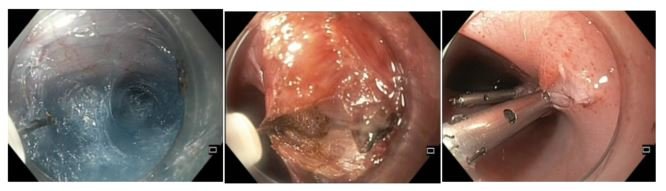
1. Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM): This is the treatment for achalasia with no surgical incision required. The procedure is done endoscopically under general anaesthesia. The endoscope is inserted into the oesophageal lumen. A tunnel is created below the inner lining of the esophagus all the way to the LES. The muscle fibres of the lower oesophagus and gastric cardia are then divided endoscopically. It is a high specialised advanced endoscopic procedure.
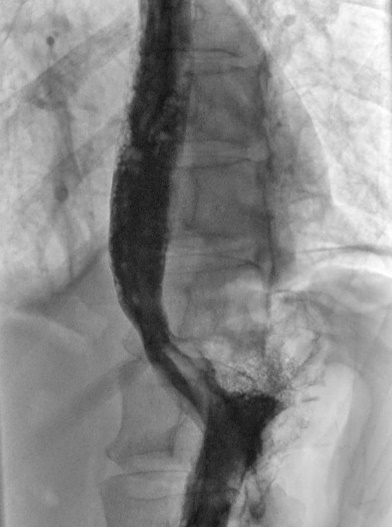
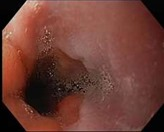
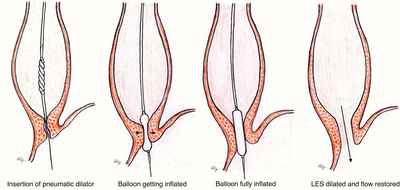
2. Balloon Dilation (Pneumatic Dilatation): A procedure where a balloon is inflated inside the esophagus to widen the lower esophageal sphincter. This procedure aims to forcefully tear the LES, hence, there can be a risk of perforation. Often, several procedures may be required to achieve good effect.
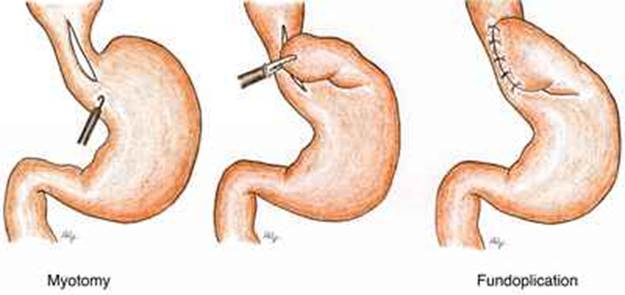
3. Heller Myotomy:A surgical procedure to cut the muscle at the lower end of the esophagus, allowing easier passage of food into the stomach. Due to the high risk of gastroesophageal reflux after this procedure, a fundoplication (wrapping the top part of the stomach around the LES) is done after the myotomy. This procedure is done under general anaesthesia. It is a minimally invasive surgery and can also be done robotically.
Several other treatments, such as Botulinum toxin (Botox) injection and medications can be given, though these options are non-definitive or temporary, and are less effective than the abovementioned options.
In severe cases (end-stage) of Achalasia, esophagectomy (removal of the entire esophagus) may be required.
Living with Achalasia
Managing achalasia involves making some lifestyle adjustments:
- Dietary Changes:Eating smaller, more frequent meals and chewing food thoroughly can help ease swallowing.
- Elevating the Head of the Bed:Sleeping with the head raised can reduce nighttime regurgitation.
- Follow-Up Care:Regular check-ups with your doctor are important to monitor your condition and adjust treatment as needed. Furthermore, patients with Achalasia have an increased risk of esophageal cancer, and should be on surveillance even after receiving treatment.
Conclusion
Achalasia can significantly impact your quality of life, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, many people experience relief from their symptoms. If you’re experiencing difficulty swallowing or other symptoms mentioned here, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Your doctor can work with you to find the best treatment plan suited to your needs.
Remember, understanding your condition is the first step towards managing it effectively. Dr. Kim Guowei, an experienced upper gastrointestinal surgeon in Singapore, specialises in managing Achalasia and can offer the abovementioned treatments. Stay informed, stay proactive, and don’t hesitate to reach out to us for support.
Book Appointment
Book your consultation today for expert surgical care.
