Gastroesophageal Reflux
Understanding the Causes and Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux, often shortened to GERD, might sound like a mouthful, but it’s a common condition that many people experience at some point in their lives. You might know it better as heartburn or acid reflux. In this article, we’ll break down what GERD is, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how to manage it effectively.
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
Imagine your digestive system as a highway, with food traveling from your mouth to your stomach. At the junction of this highway is a muscular valve called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Its job is to open to allow food into the stomach and then close to prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux occurs when this valve relaxes or weakens, allowing stomach acid to rise up into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort.
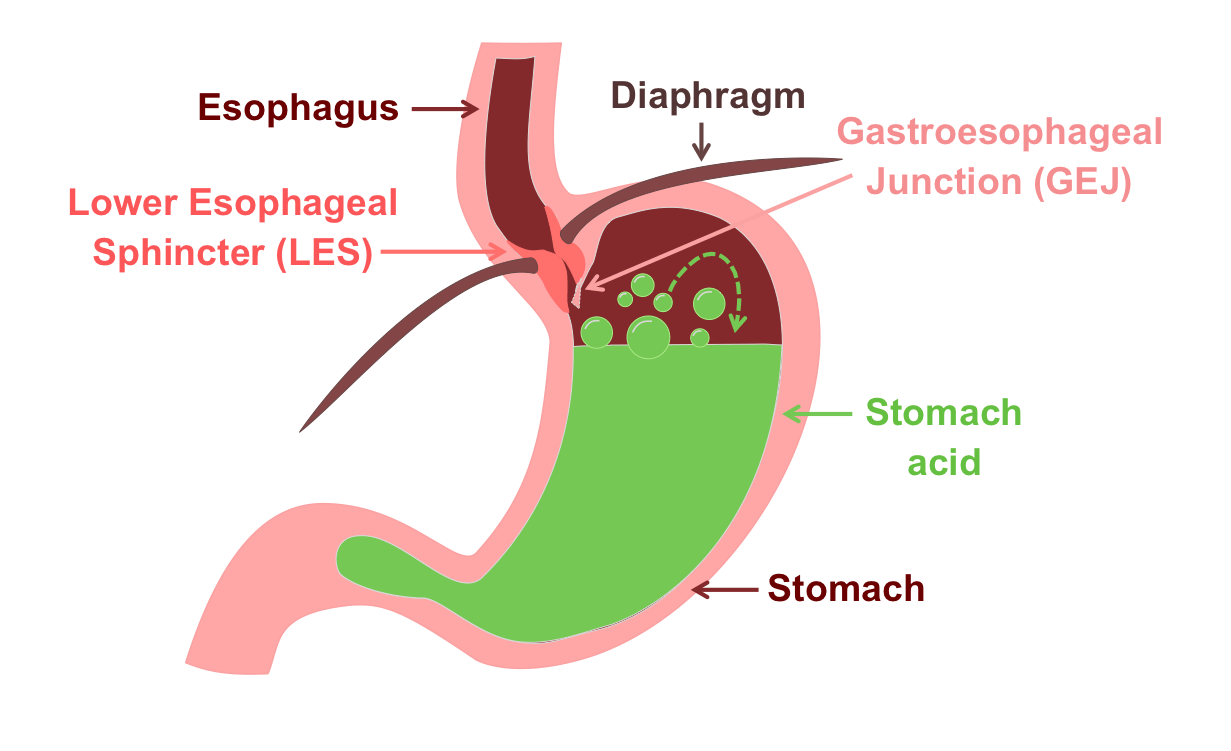
Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux:
Several factors can contribute to the development of GERD. One common cause is a weakened or dysfunctional LES, which can be influenced by genetics, lifestyle habits, and certain medical conditions. Overeating, consuming acidic or spicy foods, obesity, smoking, and pregnancy are known triggers that can exacerbate GERD symptoms.
Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux:
GERD can manifest in various ways, but the most common symptom is heartburn—a burning sensation in the chest or throat. Other symptoms include regurgitation of stomach contents, a sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and a persistent cough. These symptoms may worsen after eating, lying down, or bending over.
Diagnosis:
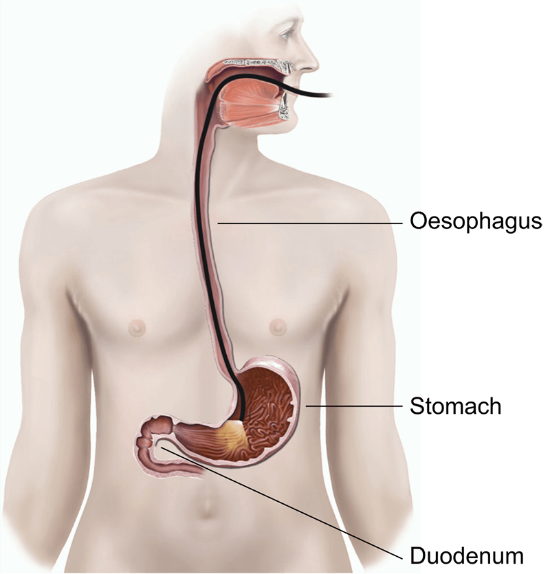
GERD can be diagnosed by symptoms and the response to medication. In some cases of GERD, inflammation of the gullet may be seen on endoscopy (a procedure when a flexible tube is placed via the mouth into the gullet and stomach)
GERD can also be diagnosed with the help of 24-hour pH monitoring. A tube is placed through the nose to the gullet and the acidity is measured.
When combined with Impedance testing (where a tube with multiple electrodes is inserted into the gullet), one can differentiate the contents of the reflux fluid, thus guiding the doctor in treatment.
Alternatively, a Bravo™ capsule can be placed during endoscopy above the LES to measure the acidity of the lower esophagus to confirm the diagnosis of GERD.

Complications of Untreated GERD:

While occasional heartburn is common and typically harmless, frequent or severe GERD symptoms can lead to complications. Chronic inflammation of the esophagus, known as esophagitis, can occur, increasing the risk of developing ulcers or strictures (narrowing of the esophagus). In some cases, untreated GERD can contribute to the development of Barrett’s esophagus, a precancerous condition.
Treatment Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux in Singapore:
The goal of GERD treatment is to alleviate symptoms, heal any existing damage to the esophagus, and prevent complications. Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing GERD. These may include:
- Dietary changes:Avoiding trigger foods such as citrus fruits, spicy foods, caffeine, and fatty foods can help reduce symptoms. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding late-night snacking can also be beneficial.
- Weight management:Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach and LES, leading to increased reflux. Losing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, or even with the help of medications or bariatric / metabolic surgery, can help alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes:Sleeping with the upper body elevated can prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus while sleeping. Avoid eating or drinking several hours prior to lying down/sleeping. Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as they can weaken the LES and increase acid production.
- Medications:Over-the-counter antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help neutralize stomach acid or reduce its production, providing relief from GERD symptoms. However, prolonged use of PPIs may have side effects and should be monitored by a healthcare professional.
- Surgery:In more severe cases or when lifestyle modifications and medications fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered to strengthen the LES and/or prevent acid reflux. Surgery usually involved performing a fundoplication. There are several types of fundoplication that can be done. Also, Fundoplication can be performed via minimally invasive or ‘key-hole’ surgery (laparoscopic or robotic). Another surgical option for patients with GERD is the LINX® anti-reflux device, a magnetic implant that can be easily placed during surgery around the LES to augment it.

The indications for intervention or surgery in the patient with GERD may include:
- Endoscopic and/or symptomatic failure of medical treatment of GERD
- Recurrence despite PPI therapy
- Volume regurgitation, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- Atypical esophageal and extra-esophageal symptoms
- Large hiatal hernias (>4 cm) (upper part of the stomach moves above the diaphragm)
- Barrett’s oesophagus
- Stricture formation (narrowing of the gullet lumen)
- Poor oesophageal peristalsis
- Prolonged reflux episodes on pH study
- Pathological bile testing
Conclusion
Gastroesophageal reflux, commonly known as heartburn or acid reflux, is a prevalent digestive disorder that can cause discomfort and interfere with daily life. While occasional heartburn can be normal, frequent or severe symptoms may indicate GERD, which requires medical attention and management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for GERD, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve their overall quality of life. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe GERD symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment. Don’t hesitate to reach out to our clinic at Crest Surgical Practice in Singapore.
For more information or to schedule an appointment with Dr Kim Guowei, our general surgeon who subspecialises in upper gastrointestinal surgery in Singapore, please contact us today. With the right approach, GERD can be effectively managed, allowing you to enjoy a more comfortable and symptom-free life.
Book Appointment
Book your consultation today for expert surgical care.
